Nucleosides and Nucleotides
| DNA Structure | Table of Contents |
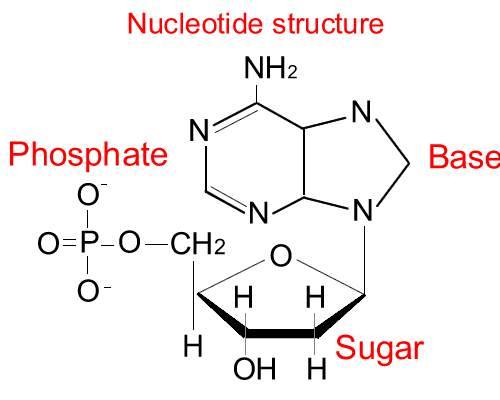
A nucleotide is composed of a sugar (ribose in RNA, deoxyribose in DNA), a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group. The structure formed by the sugar and the base is called a nucleoside; the nucleotide is formed when the phosphate group is attached. Nucleotides can be in the monophosphate, diphosphate or triphosphate form. The general structure of a monophosphate nucleotide is:
|
|
The five nucleotides that are common in DNA and RNA are shown here. It is important to know the general difference between the two purine bases, which have a double ring structure, and the two pyrimidine bases which have a single ring structure.
|
|
The names for the common bases, nucleosides and nucleotides are given in the table:
| Base | Nucleoside | Nucleotide |
| Adenine | Adenosine | Adenosine Triphosphate |
| Thymine | Thymidine | Thymidine Triphosphate |
| Guanine | Guanosine | Guanosine Triphosphate |
| Cytosine | Cytidine | Cytidine Triphosphate |
| Uracil | Uridine | Uridine Triphosphate |
A triphosphate nucleotide is designated by dNTP or NTP depending on whether it has a deoxyribose (dNTP) or ribose sugar. The N indicates "base" and when the base is known the single letter code is used:
| Base | deoxy Nucleotide | Nucleotide |
| Adenine | dATP | ATP |
| Thymine | dTTP | TTP |
| Guanine | dGTP | GTP |
| Cytosine | dCTP | CTP |
The monophosphate and disphosphate forms are designated by NMP and NDP respectively.
There are other bases, and corresponding nucleotides, that are found in cells, sometimes due to mutation and sometimes due to processing by the cells itself that you will see referenced. Here are some of them.
| Base | Similar to |
| Hypoxanthine | Guanine |
| Inosine | Guanine |
| Xanthine | Guanine |
| DNA Structure | Table of Contents |